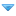
Exceptions and Errors fall into three categories: checked exceptions, unchecked exceptions, and errors.
Checked Exceptions
Checked by the compiler at compile time
Methods that throw checked exceptions must indicate so with throws which must propagate up the calling stack until the exception is handled
Checked exceptions require explicit catching with a catch block
These include exceptions of the type Exception, except for RuntimeException and its subtypes
Unchecked Exceptions
Not checked at compile time by the compiler
Occur during runtime due to programmer error (i.e. out-of-bounds, divide by zero, etc.) or system resource exhaustion
These do not have to be caught (as they are not checked, they only are known when they occur)
Methods may throw unchecked exceptions but do not have to indicate so in declaration
These are exceptions and subtypes of RuntimeException
Errors
Errors are typically unrecoverable and present serious conditions
Errors are not checked at compile time and do not have to be (but can be) caught or handled
Checked Exceptions
Checked by the compiler at compile time
Methods that throw checked exceptions must indicate so with throws which must propagate up the calling stack until the exception is handled
Checked exceptions require explicit catching with a catch block
These include exceptions of the type Exception, except for RuntimeException and its subtypes
Unchecked Exceptions
Not checked at compile time by the compiler
Occur during runtime due to programmer error (i.e. out-of-bounds, divide by zero, etc.) or system resource exhaustion
These do not have to be caught (as they are not checked, they only are known when they occur)
Methods may throw unchecked exceptions but do not have to indicate so in declaration
These are exceptions and subtypes of RuntimeException
Errors
Errors are typically unrecoverable and present serious conditions
Errors are not checked at compile time and do not have to be (but can be) caught or handled