Environment variables in QTP are like global variables in other programming languages which can be accessed through any part of the script. The values of these variables remains same irrespective of the number of iterations (unless you change them through scripting). These variables can prove to be very useful when you want a variable to be shared across various reusable actions.
There are two types of environment variables:
- Built-In: These are the internal variables that are provided by QTP. Among others they can provide you valuable information like the path of the folder where test is located, the path of the results folder, the name of the action iteration or the OS version. So, how can we access the built in environment variable? It’s simple, just have a look at screenshot.
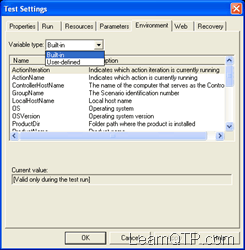 So if you want to know the OSVersion of the operating system where your test is running. You can simply type in Environment.Value(“OSVersion”)
So if you want to know the OSVersion of the operating system where your test is running. You can simply type in Environment.Value(“OSVersion”)
- User-Defined: These can be further defined into two types.
- User defined Internal
- These are the variables that we define within the test.
- These variables are saved with the test and are accessible only within the test in which they were defined.
- So how can we define and use them?
To define them: Environment.Value(“name”)= “Ankur Jain”
To call them: msgbox Environment.Value(“name”)
- User defined External
- These are the variables that we predefine in the active external environment variables file.
- These can be created using a list of variable-value pairs in an external file in .xml format. This is a topic of a separate post that we will discuss later.
- User defined Internal







Hello Ankur
I want to be able to assign values from my global datatable to userdefined env. variables and have it as an input for my second action how is this achieved.
can you please describe in between global and environment variable in qtp and provide some basic info when we go specific to env/global variable
@Tirumala: What global variables are you referring to here?
hello, Ankur
i have read a lot of the work you put out on your blog, very helpful for beginners like my self, i am wondering if you would help me in a one o one basis untill i get in my feet. willing to arragne $ometing
Environment variable like the application executable and path; URL of web application etc. Do I put in Built-in or User-defined?
W.R.T.
1) When you want a global variable that is needed throughout the test run (across all your reusable actions).
If the variable/set of data is stored in an external Excel Data sheet. How can we make use of Environment Variable in that case?
ALM connected to UFT.Loading env file from ALM directory.Getting error ‘file not found’
How to apply the if condition inside the environment variable xml file.
I have two variable in xml file
SendMail
Y
Now I want if the sendmail variable value is Y then load the 2 nd variable otherwise not load the variable.
@Narendra: XML primary purpose is to store and carry data. I don’t think you can put any processing logic inside the file. Why don’t you do this check outside? For follow up, please open a thread at UFT forums.
Hi Ankur,
1. Can we send the mail using html tags and javascript
2. Can we send the mail with donut chart
Hi All,
I want make one variable as global, which can be used in different Tests (not in actions)..
without using external xml file. can we store one variable within QTP settings..
if we have option can someone post me..
Thank you,
Santhosh
Can any body tell me how to get no. of same results from an external environment variable.
i used environment.loadfromfile(“D:\..xml”)
then environment.value(“…”)
but i want to extract all results to display?can any body help to find out
Hi sir,
1.In real time project how to use environment variable and the recovery scenario.
2.To review the testcase what are the document you are using
Hi Ankur,
I’m looking for way to get run context to pull user profile for URL/Project/Username/passsword, like it allow with Service Test. Do you have any idea how to do it?
Thanks,
Hi Ankur,
Could you mention the post where you have suggested using external environment variables in QTP?
hi,
can anyone tell me how to change environment variable during runtime?
Hi Sreshta,
Yes this can be done definitely. You can define this in a .vbs file say commonfunction.vbs
write the below code say
Set Obj_SelCust=Description.Create()
Obj_SelCust(“Micclass”).Value=”WebList”
Obj_SelCust(“name”).Value=”customerId”
now save this file
this object Obj_SelCust can be used anywhere in the script all you have to do is add this vbs file in your script.
Hi Sridevi,
Do you mean to say you want to clear all the variables
such as Environment.Value(“x”)=10
so now you want to make this null
Is that your question?
HI Ankur,
I want to Delete or clear the memor of all the environmental variable that we use in the code ibnce the execution is completed. Could you let me know how we can do this?
Hi Ankur,
Is there anyway to set a object and use it globally throughout all test script and functions.
Environment variable can help upto setting a variable level.
What if i need a object which we can use it globally for all functions.
eg- Set objRep = CreateObject(“Mercury.ObjectRepositoryUtil”)
I need to hold the “objRep” till the run time of test script otherwise it’ll stop the test as soon as I set it to “Nothing”.
Who is using QTP now?
How to read name/value pairs in xml file in QTP
‘
‘
‘
‘ m
‘ 55
‘
‘
environment file is:
m
55
below code will give u some idea about environment variables:
Dim i,j,c,d
i=environment(“OS”)
j=environment(“OSVersion”)
print i
print j
c=environment.value(“a”)
print c
d=environment.value(“b”)
print d
environment.LoadFromFile(“C:\Documents and Settings\SIVA\Desktop\env1.xml”)
e= environment.value(“m”)
msgbox e
msgbox environment.ExternalFileName
msgbox environment.Value(“gg”)
environment.Value(“gg”) =15
msgbox environment.Value(“gg”)
environment file:env1.xml
m
55
@Bharat…Check your spelling. You forgot the ‘r’ in “OSVersion”.
Can we use the below code in the VBS file(without QTP installed)?
Msgbox Environment.Value(“OSVesion”).
I tried it but getting the ‘object required ‘ error
Pls help me
Can we use all the variable as “Environment variable” while doing scripting.
Reason:
1. We might use those variables in more than one Action.
2. We might use those variables in more than one Test cases.
3. Instead of declaring the variable again and again, then avoiding declaring with data types, we can use Environment.Value(“Variable Name”).
4. If we declared it in Driver script we no need to declare in other Actions too.
Please let me know your valuable comments.
Thanks & Advance,
Dhanavantha. G
Answer to Nandana’s question
Object Required: Environment
You have created a new script so you need go to the Test Settings –> Environment –> Load the file
This should help
i NEED TO CAPTURE CURRENT SYSDATIME IN ENVIRONMENT ..
i TRIED :
Environment.Value(“DateTime”)=now
msgbox environment.Value(“Datetime”)
pLEASE HELP
hi,
I have used the Built in environment variable to get the Wks Id. The code is
VPCID = Environment.Value(“LocalHostName”)
This used to work in my old scripts. But in the new scripts, following error is recieved.
Object Requirred: Environment
Do you have any idea why this error is recieved? Thanks
I need this ASAP.
Hi, can u tell me is there any way by which I can store a varriable in a test case & use it in another one.
well written !!!
Suppose I want to list all environment variables, programatically within my script, so I know everyting that is loaded and available to me. How might I do this?
Hello Ankur,
How about if we apply Environment value in localized/globalized application? Looking forward to hearing your advice. Thanks in advance.
to the above question ..
You can import only one xml file.
so club both the xml into one xml and import those.
Let me knwo for more info.
In my above post I had put all the closed tags required. Basically it works with one Name = Value pair and not two.
Hi,
I am a beginner and tried to experiment with Environment Variables in QTP. I have a doubt here. Donno if this works like this or I am missing something or z it a bug.
My Environment XML file 1 is:
Test
I am here
Environment XML file 2 is
Test
I am here
Test2
Blah blah
1. While loading User defined- External environment variables either at run time or through File->Settings->Environment for file 2 nothing works and it gives me errors as expected because it fails to read the variables form files et al.
2. Works as desired for File 1.
My Ques is same: Is it supposed to work like this or am I missing something on this?
[i]
what ia the diff between in below two statements
1.environment.value(“x”)=10
2.environment(“x”).value=10
[/i]
environment(“x”).value=10–> Value stored in this variable cant be reassigned/change/update to any other value…
Ankur can you please explain how to use the action1 variable or action1 env variable in Action2? I tried like this. In action1 i decalred variable and tried to use the same in action2. but i am getting blank value. Can you please give the solution apart from using the Global variables.
Hey Zaki,can u be more clear as to what you want to do,whether you want to iterate or not,2nd->user defined environment variable are read only.
hi Ankur,
Could u plz tell me where exactly we’ll b using checkpoints and output values and difference b/w them
Hi!! I am new to QTP. I fell into a situation where the iterations kept on importing the excel sheet and hence for every iteration the first row was read even though I checked …Run on all rows. Hence I thought of using user-defined environment variable to fix the problem. At the end of the run I also found that the variable retains its original value at the end of the test. Here is the code if it helps:
x = Environment.Value(“Imp”)
If x=0 Then
DataTable.Import(“D:\Documents and Settings\Zaki\Desktop\Expression.xls”)
End If
Window(“Calculator”).WinButton(“C”).Click
Window(“Calculator”).WinEdit(“Edit”).Type DataTable(“Expression”, dtGlobalSheet)
result=Window(“Calculator”).WinEdit(“Edit”).GetROProperty(“text”)
DataTable(“Actual”,dtGlobalSheet)=result
DataTable.Export(“D:\Documents and Settings\Zaki\Desktop\Expression.xls”)
Environment.Value(“Imp”)=1
How to persit environment variables data after the script run. Currently the environment variables data is available only during the run session
Hi,
Please help me understand the difference between global variable and environment variable?
are these same?
Hi Ankur,
How can I change the value of user defined external environment variable, in a test script, and still make new valule accessible across test scripts and libraries ?
Thanks
Abhishek
Hi Ankur,
I too had the same doubt. can you please answer me.
I need to increment the user defined external variable by one in different reusable actions. If suppose the variable a is the external variable with value as 0. i need to use this variable 10 times in different reusable actions then the variable a in the main action should return 10. Is this possible?
Hello Ankur,
I am executing QTP scripts from VB Script.
however I am not able to import the environment variable xml file in QTP so that the those variable values will be used in scripts..
could you please help me??
I have a scenario whereI have used an environment variable env1 in10 data sheets.
Please suggest how to call all of them into one script.
what ia the diff between in below two statements
1.environment.value(“x”)=10
2.environment(“x”).value=10
What bothers me is how can I change external variables within a script? (e.g. using VBScript)
Since they are read only they can only be changed outside the script.
But what if I need to run a bunch of tests, sometimes with one value and sometimes with another.
E.g. Today I run them all on site
https://www.macys.com/.Tonight I want to run them on both
sales.macys.comandinventory.macys.comWith External Environment variables there is no way to change them programmatically (e.g. at nite when running unattended).
With Internal variables, they can only be set from inside the test.
Here I want to set an enviornment and let it run at night. Then change it and again run using a differnt value unattended at night, and have all tests take the same Environment variable.
Thanks Ankur.
Hey Ankur,
User defined external variables in .xml realy help me a lot, Thanks a BUNCH
I need some help in updating the external variables to .xml, can you please help me with this?
HI Ankur ,
This regarding enviromental variables. How this variables are different from dim variables declared.
And main thing you didnt explain us how to declare a variable that can be used outside the script action. That is how to declare a variable as global.
Difference lies in the scope, environment variables are available throughout all your actions during a script run. Check the ‘User Defined’ part above for how to define environment variables.
We can use environment variables in a number of ways:
1) When you want a global variable that is needed throughout the test run (across all your reusable actions).
2) When you see that one reusable action in a script is dependent on the others. You might want to use them
3) When you need to reference the current “test directory” irrespective of the location where it is stored.
…there can be many many more useful applications.
Having said that, there can be many ways through which you can accomplish the same task.
A simple ex: what you do with a switch statement can also be done with if-else but sometimes using if-else might not be as efficient and the code won’t look readable.
It boils down to the fact that you need to find the most optimum solution for a given problem.
Hi Ankur,
I do agree with yo blog about Environment variable. but what’s the use? Can you give a realtime example where environment variable (user defined) is almost required.
Nirmal